概述
此文用于记录学习 HackTheBox 网站中 Path: Junior Cyber security Analyst 获得的知识点。ƪ(˘⌣˘)ʃ
Path’s Modules
Module 1: Introduction to Information Security
Section 1: Structure of InfoSec
Section 2: Principles of Information Security
Section 3: Network Security
Section 4: Application Security
CIA:confidentiality, integrity, and availability,机密性、完整性与可用性。
Section 5: Operational Security
Section 6: Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
DR\BR:Disaster Recovery/Business Continuity,灾难恢复/业务连续性。
Section 7: Cloud Security
Section 8: Physical Security
Section 9: Mobile Security
Section 10: Internet of Things Security
Section 11: Distributed Denial of Service
DDoS:Distributed Denial of Service,分布式拒绝服务。
Section 12: Ransomware
Section 13: Social Engineering
Section 14: Insider Threat
Section 15: Advanced Persistent Threats
APT:Advanced Persistent Threats,高级持续性威胁。
Section 16: Threat Actors
Section 17: Red Team
Section 18: Blue Team
Section 19: Purple Team
Section 20: Chief Information Security Officer
CISO:Chief Information Security Officer,首席信息安全官。
Section 21: Penetration Testers
Section 22: Security Operations Center
SOC:Security Operations Center,安全运营中心。
Section 23: Bug Bounty Hunter
Section 24: Recommendations
Module 2: Network Foundations
Section 1:Introduction to Networks
LAN/WAN:局域网/广域网。
什么是网络?:网络是可以互相通信、接发数据的设备的集合,其主要有以下部分构成:
| 概念 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Nodes | 连接到网络的单个设备 |
| Links | 连接两个 Node 的通信路径 |
| Data Sharing | 网络的目的是实现设备间的数据交换 |
局域网:小范围的网络,连接短距离内的设备,其具有以下特点:
| 特点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Resource Sharing | 占地面积小 |
| Ownership | 通常属于个人或单个组织 |
| Speed | 数据的传输速率高 |
| Media | 通信路径连接的媒体,通常是以太网电缆或 Wi-Fi |
广域网:连接多个局域网的网络,最大的即是互联网,较局域网而言,数据传输较慢、通信路径载体多为光纤、卫星等。
以如下图展示局域网及广域网的基本结构:
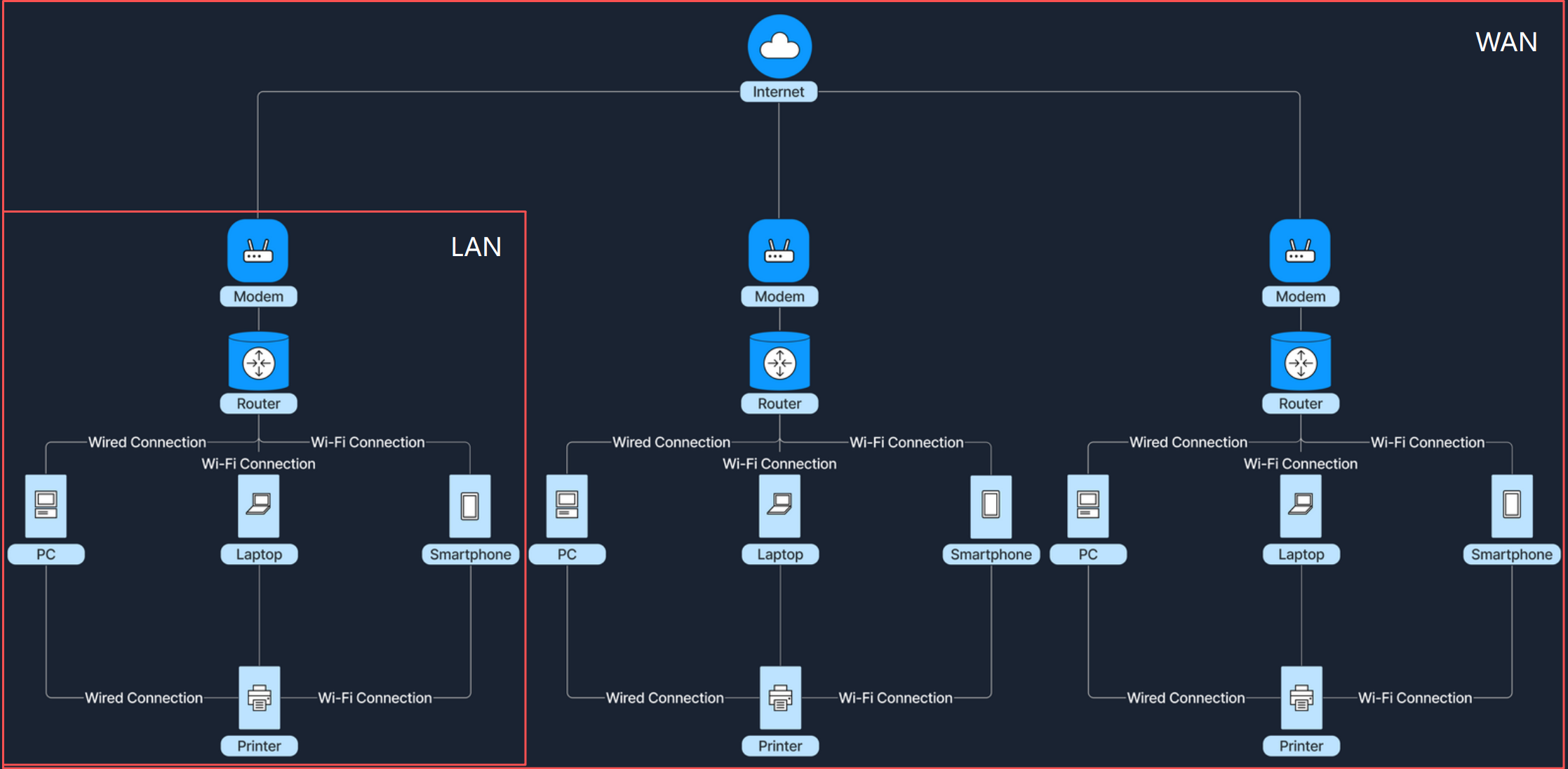
Section 2: Network Concepts
OSI Model:Open Systems Interconnection Model,将电信或计算系统的功能标准化为七个抽象层。
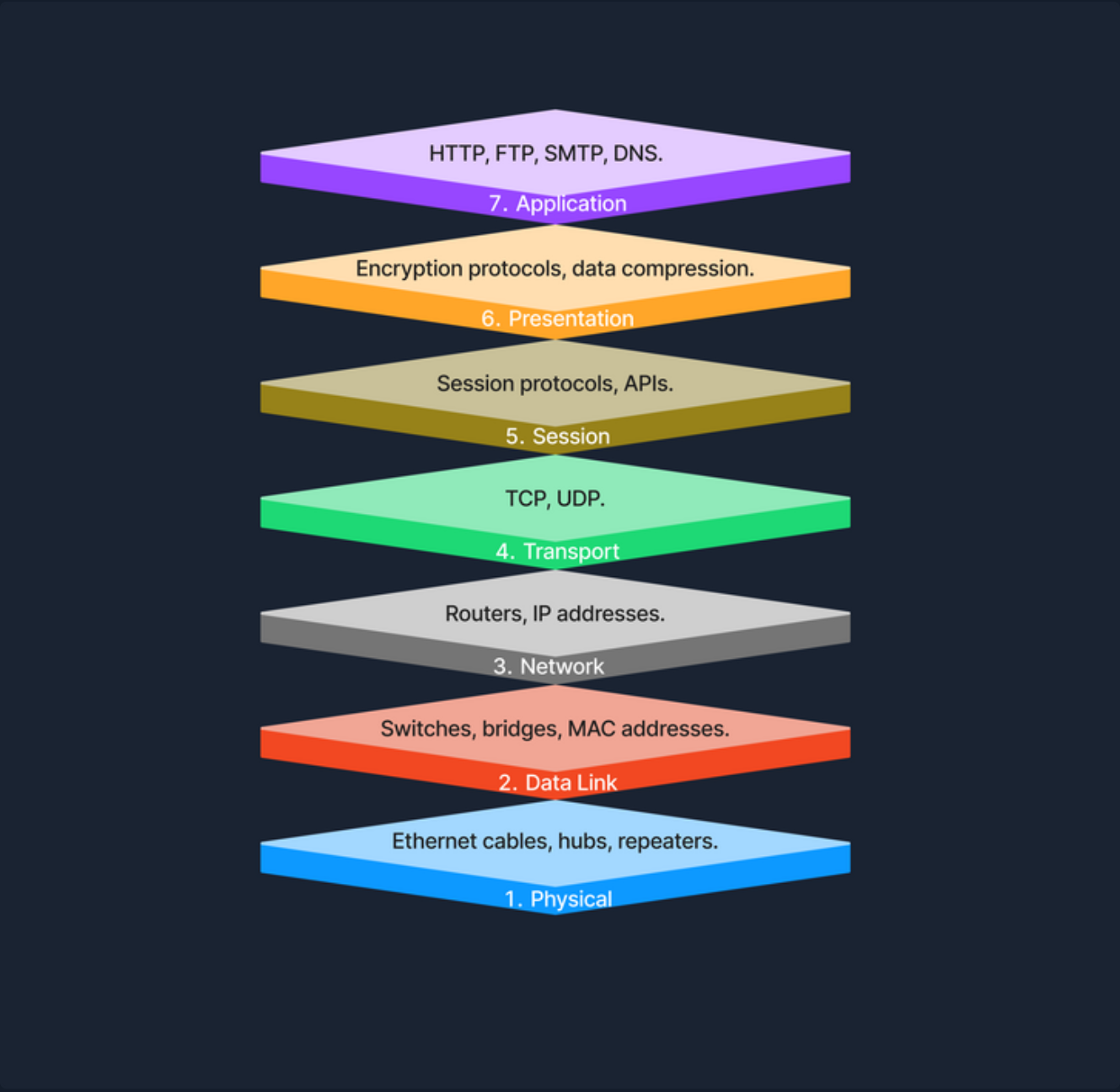
| 抽象层 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 物理层 | 负责在物理介质上传输原始比特流,处理设备之间的物理连接,包括以太网电缆、集线器、中继器等硬件组件。 |
| 数据链路层 | 提供节点到节点的数据传输,确保数据帧的同步、错误检测与纠正。交换机和网桥工作在该层,使用 MAC 地址识别网络设备。 |
| 网络层 | 负责分组转发和路由选择,使用 IP 地址进行逻辑寻址,确保数据能跨越多个网络到达正确的目的地。路由器在该层工作。 |
| 传输层 | 提供端到端通信服务,负责数据的可靠或不可靠传输、分段、重组、流量控制和错误校验。常用协议有 TCP(可靠、面向连接)和 UDP(快速、无连接)。 |
| 会话层 | 管理应用之间的会话,负责建立、维护和终止连接,并支持会话检查点与恢复,保证中断后通信可恢复。 |
| 表示层 | 作为应用层与网络格式之间的翻译者,处理数据表示、加密解密、压缩和格式转换,保证跨系统数据可读。 |
| 应用层 | 直接为终端用户应用提供网络服务,如资源共享、远程文件访问。常见协议包括 HTTP、FTP、SMTP、DNS 等。 |
TCP/IP Model:Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol Model,简化 OSI Model 为四层。
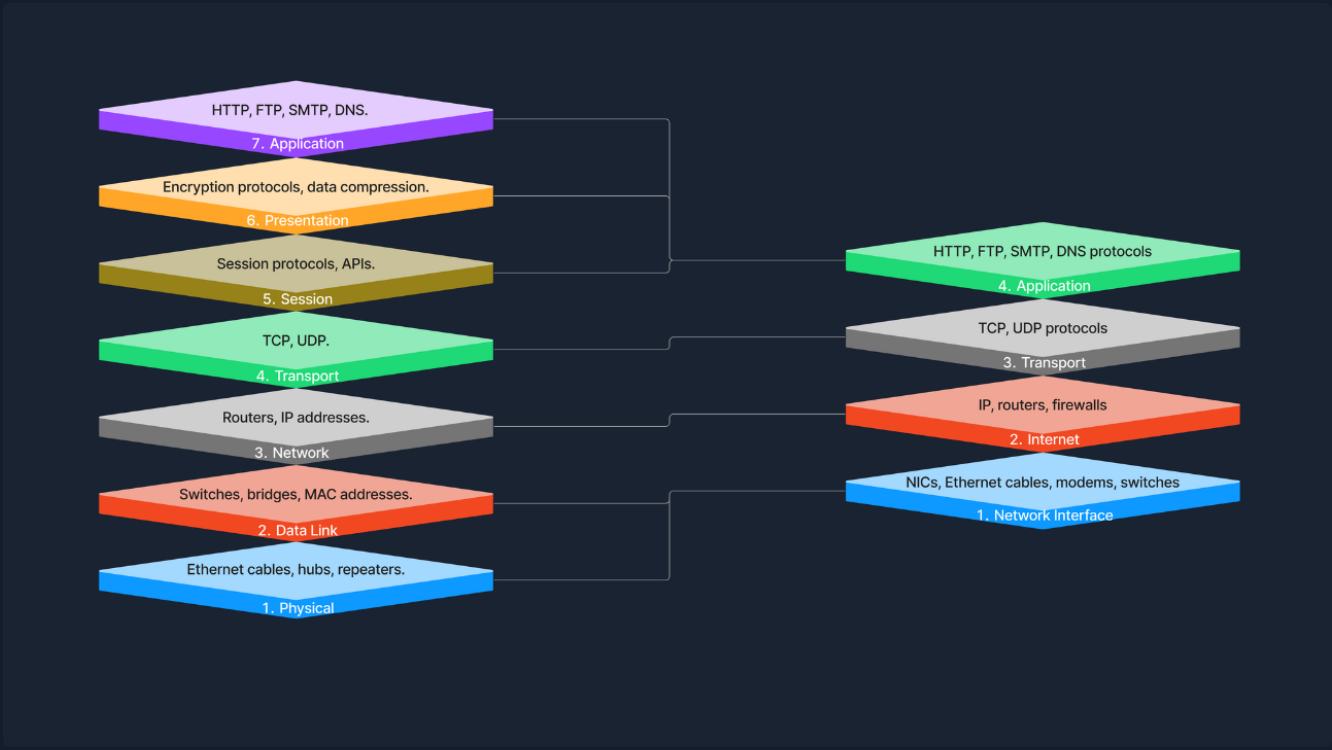

| 抽象层 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 链路层 | 负责处理网络硬件和介质的物理方面,包括以太网(有线)和 Wi-Fi(无线)等技术。对应 OSI 模型的物理层和数据链路层,涵盖从物理连接到数据帧的处理。 |
| 网际层 | 负责设备的逻辑寻址和跨网络的数据包路由,常用协议有 IP(互联网协议)、ICMP(互联网控制报文协议)。确保数据包通过逻辑路径到达正确目的地,对应 OSI 网络层。 |
| 传输层 | 提供端到端通信服务,确保数据包按序且无误传递。TCP 提供可靠、面向连接的通信,UDP 提供快速、无连接的服务。对应 OSI 传输层。 |
| 应用层 | 包含直接为应用提供服务的协议,如 HTTP(网页浏览)、FTP(文件传输)、SMTP(电子邮件)。对应 OSI 的会话层、表示层和应用层,提供数据交换的接口与协议。 |
网络传输:即指通过介质将数据信从一台设备发送到另一台设备的过程。
传输类型:分为模拟和数字两种,模拟传输使用连续变化的波形传输信息,多用于无线电广播;数字传输使用 0/1 比特位传输信息,多用于计算机网络中。
传输模式:分为 Simplex、Half-duplex 和 Full-duplex三种模式。
| 模式 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Simplex,单工 | 仅允许单向通信 | 键盘到计算机 |
| Half-duplex,半双工 | 允许双向通信,但不能同时进行 | 对讲机通话 |
| Full-duplex,全双工 | 支持双向同时通信 | 电话通话 |
传输介质:在网络中传输数据的物理方式,有线(光纤等)或无线(Wi-Fi、红外遥控器等)。
Section 3: Components of a Network
网络组件:分为以下四部分:End Devices,终端设备;Intermediary Devices,中间设备;Network Media and Software Components,网络媒体和软件组件;Servers,服务器。
End Devices:接发数据的设备,电脑、手机、平板均是。
Intermediary Devices:主要介绍三种,网卡、路由器和交换机:
| 中间设备 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Network Interface Cards(NICs),网络接口卡 | 用于连接到网络,如通过电缆连接的以太网卡,或者是利用无线电波的 Wi-Fi 适配器。每个网卡拥有一个 MAC地址。 |
| Routers,路由器 | 读取数据包中的网络地址信息以确定其目的地,使用路由表和路由协议 Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)来查找数据间传递的最有效路径。 |
| Switches,交换机 | 连接同一网络内的多个设备,使用 MAC 地址仅将数据转发给预期的接收者,比如员工发送资料至打印机。 |
Network Media and Software Components:网络媒体(电缆和连接线)和网络协议(如 TCP/IP 等)不再说明,主要说明软件防火墙:
1 | Software Firewalls |
Servers:服务器通常运行专门的操作系统,这些操作系统经过优化,以处理多个同时请求。
Section 4: Network Communication
MAC Address:每个 MAC 地址长 48 位,通常以十六进制格式表示,显示为六对十六进制数字,用冒号或连字符分隔,例如 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E。其前 24 位代表分配给制造商的地址 Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) ,而其余 24 位则特定于单个设备。
MAC 地址的使用:MAC 地址是局域网内本地通信的基础,用于将数据帧传送到正确的物理设备,其具体通信过程如下:
1 | data + destination MAC -> a data frame |
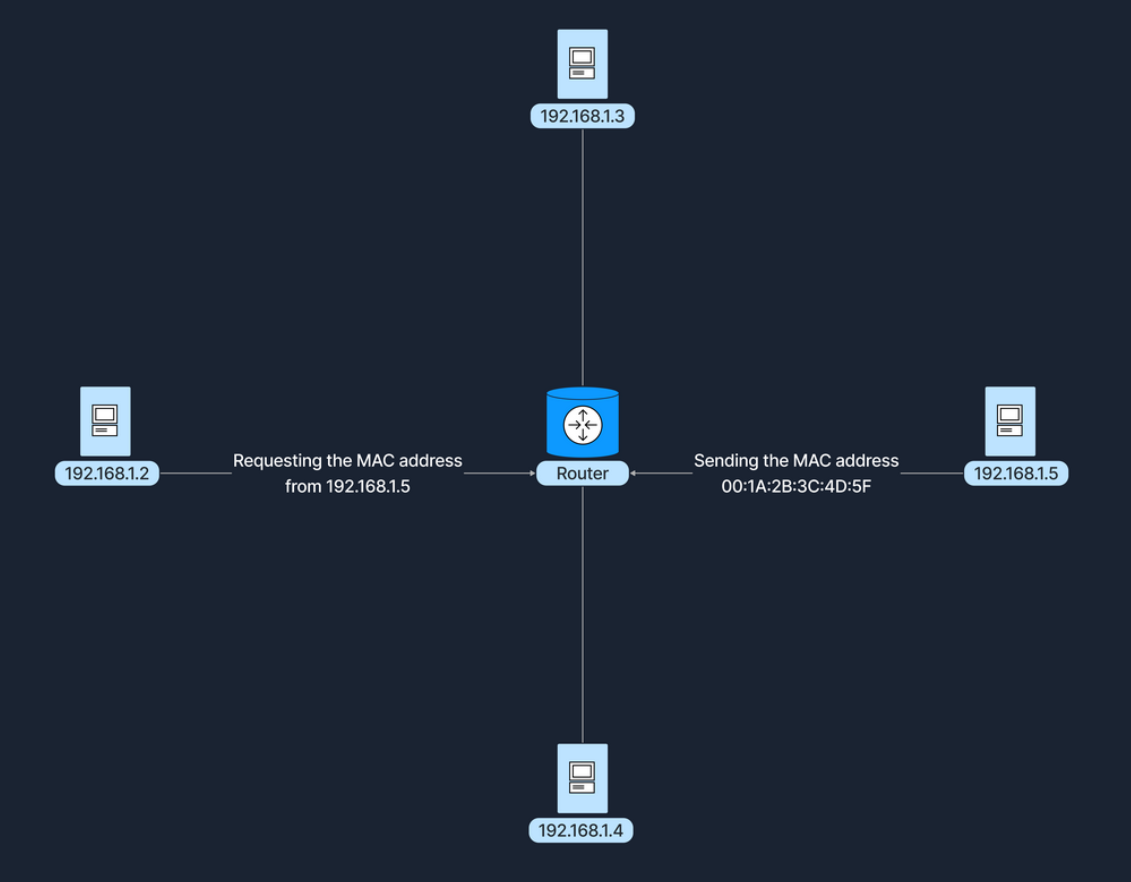
此外,还可以通过 Address Resolution Protocol(ARP)协议将 IP 地址映射到 MAC 地址,允许设备找到与同一网络内已知 IP 地址关联的 MAC 地址,如下图所示:
IP/Port:具体格式不再解释,这里记录一个检测、侦听端口的指令:netstat。
访问网站的具体步骤:如下所示
1 | 1、输入目标域名 A |
Section 5: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
DHCP 简介:自动执行在 IP 网络上配置设备的过程。它允许设备自动接收 IP 地址和其他网络配置参数,例如子网掩码、默认网关和 DNS 服务器。
DHCP roles:即 DHCP Server 和 DHCP Client:
| 角色 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| DHCP Server | 管理 IP 地址分配的网络设备(如路由器),维护一个可用 IP 地址和配置参数的池。 |
| DHCP Client | 连接到网络并从 DHCP 服务器请求网络配置参数的任何设备。 |
DHCP 工作原理:称为 DORA, 即 Discover、Offer、Request 和 Acknowledge.
| 步骤 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Discover(发现) | 当设备连接到网络时,它会广播 DHCP Discovery 消息以查找可用的 DHCP 服务器。 |
| Offer(提供) | 网络上的 DHCP 服务器接收发现消息并使用 DHCP Offer 消息进行响应,向客户端建议 IP 地址租约。 |
| Request(请求) | 客户端收到提供并回复 DHCP Request 消息,指示它接受提供的 IP 地址。 |
| Acknowledge(确认) | DHCP 服务器发送 DHCP Acknowledge 消息,确认已为客户端分配了 IP 地址。客户端现在可以使用该 IP 地址在网络上进行通信。 |
在租约到期之前,客户端必须主动尝试续订其 IP 地址租约。这涉及向 DHCP 服务器发送续订请求。当租约接近到期时,客户端与 DHCP 服务器通信,询问它是否可以继续使用分配的 IP 地址,服务器可以肯定地响应该地址,从而延长租约。

Section 6: Network Address Translation (NAT)
公共 IP:由互联网服务提供商 (ISP) 分配的全局唯一标识符。配备这些 IP 地址的设备可以从互联网上的任何位置访问。
私有 IP:这些地址在全球互联网上不可路由,这意味着发送到这些地址的数据包不会由互联网主干路由器转发。
NAT:Network Address Translation,网络地址转换,使本地网络可以在共享单个公共 IP 地址的同时使用私有 IP 地址,是由路由器或类似设备执行的过程。
NAT 工作原理:即令路由器携带共享的公有 IP,在局域网设备需访问公有 IP 时,首先将数据包发送给路由器,路由器在修改源私有 Ip 后,再进行发送,如下图所示:
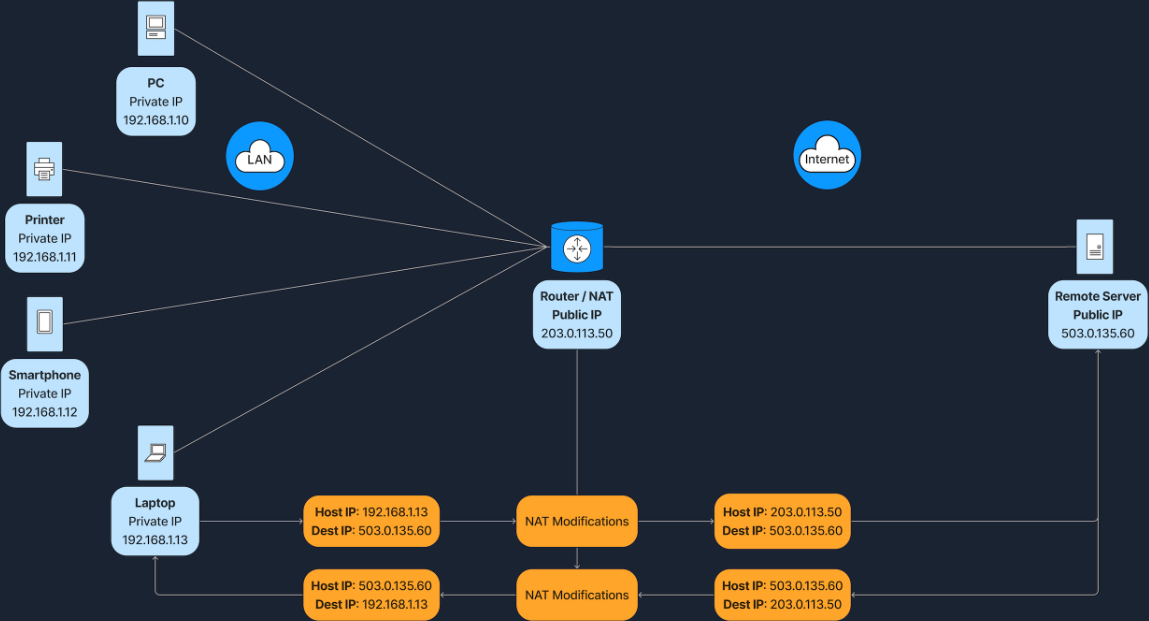
NAT 类型:如下表所示:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 静态 NAT | 涉及一对一映射,其中每个私有 IP 地址直接对应于一个公共 IP 地址。 |
| 动态 NAT | 根据需要,根据网络需求将可用地址池中的公共 IP 分配给私有 IP。 |
| 端口地址转换(PAT) | 也称为 NAT 过载,是家庭网络中最常见的 NAT 形式。多个私有 IP 地址共享一个公共 IP 地址,通过使用唯一的端口号来区分连接。这种方法广泛应用于家庭和小型办公室网络,允许多个设备共享一个公共 IP 地址进行互联网访问。 |
Section 7: Domain Name System (DNS)
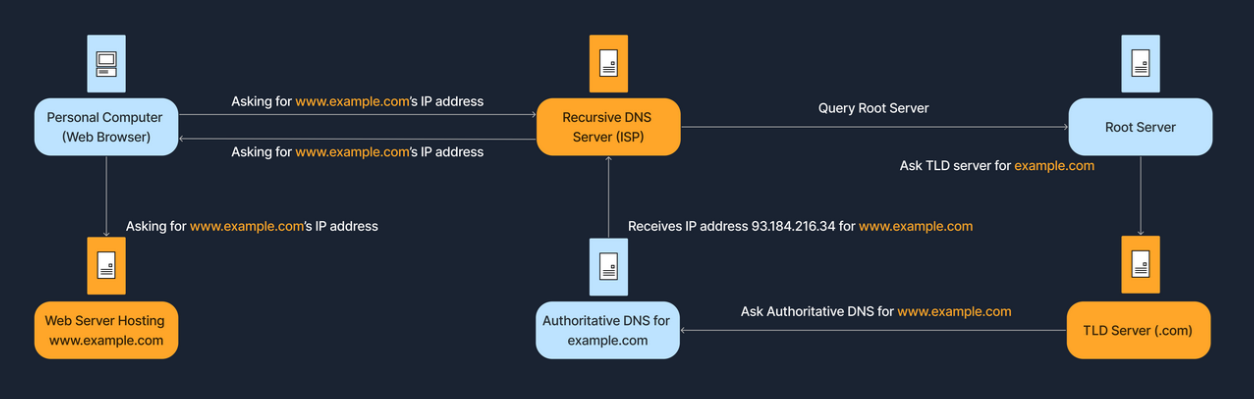
DNS 层次:分为 Root Servers(根服务器)、Top-Level Domains (TLDs,顶级域名)、Second-Level Domains(二级域名)和 Subdomains(子域名),如下图所示:

DNS 查询过程:如下图所示:
Section 8: Internet Architecture
P2P Architecture:点对点架构每个节点,无论是计算机还是任何其他设备,都充当客户端和服务器。这种设置允许节点直接相互通信,而无需中央服务器。
Client-Server Architecture:客户端-服务器架构,客户端(即用户设备)发送请求,例如 Web 浏览器请求网页,服务器响应这些请求,例如托管网页的 Web 服务器。此时,这些服务器充当网络的中心,并托管网络的部分数据。
Single-Tier Architecture:单层体系结构,客户端、服务器和数据库都驻留在同一台计算机上。
Two-Tier Architecture:双层体系结构,客户端处理表示层,服务器管理数据层。此模型通常出现在桌面应用程序中,其中用户界面位于用户的计算机上,而数据库位于服务器上。通信通常直接发生在客户端和服务器之间。
Three-Tier Architecture:三层体系结构,相较前一体系,将数据库单独作为第三层。在这个模型中,客户端管理表示层,应用程序服务器处理所有业务逻辑和处理,第三层是数据库服务器。
N-Tier Architecture:略。
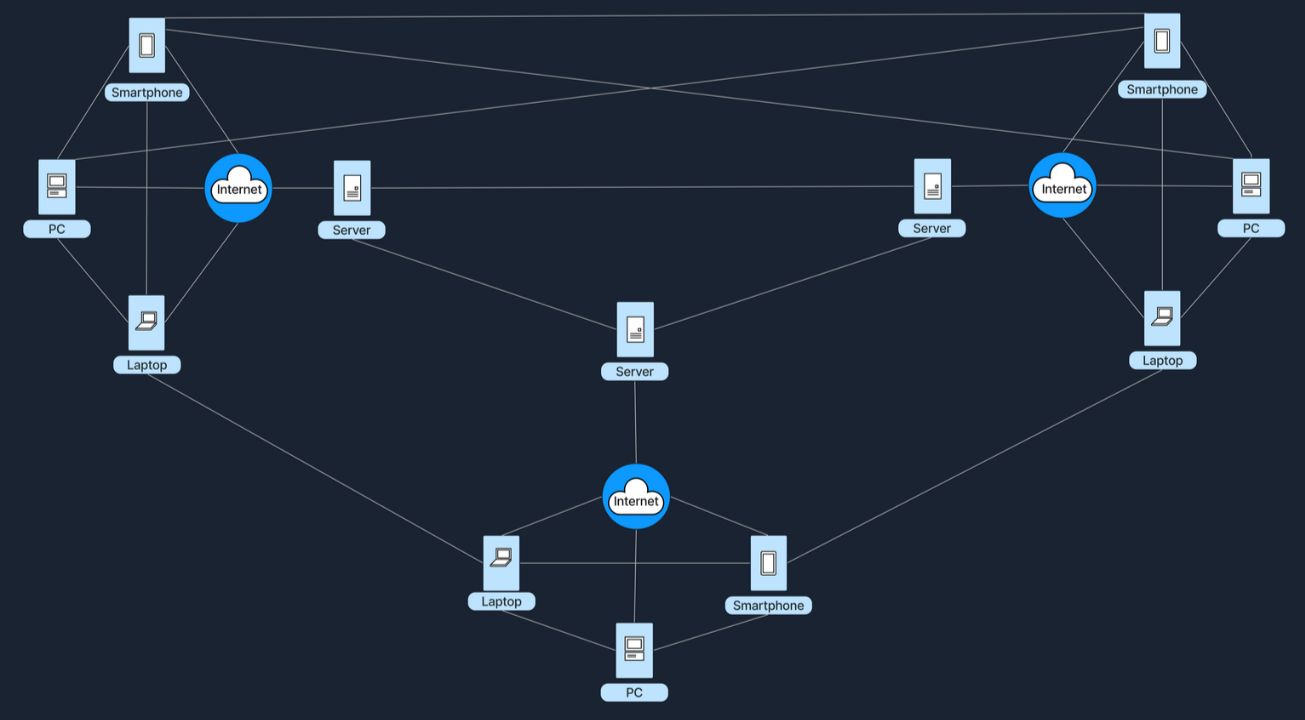
Hybrid Architecture:混合模型,在此设置中,中央服务器用于促进协调和身份验证任务,而实际数据传输则直接在对等方之间进行。以下是其结构示意图:
Cloud Architecture:云架构,此体系结构遵循客户端-服务器模型在虚拟化规模上运行。而计算的基础设施由云服务商提供。
Software-Defined Architecture (SDN):软件定义架构,其将功能分至两个平面:控制平面,决定数据的传输方向;数据平面,执行数据传输。传统的路由器和交换机均拥有此两平面的功能,SDN 则提取其中控制平面功能并移至称为控制器的中央计算机程序,而路由器和交换机仅需执行控制器下发的指令,也即传输数据至指定位置。
Section 9: Wireless Networks
Wireless Router:无线路由器。其定期发送特定频率的无线信号(称信标帧),设备监听不同频率的信道,以发现身边的路由器,通过身份验证后成功同无线路由器连接。而路由器则插入调制解调器,该调制解调器从 ISP(互联网服务提供商)提供互联网服务。
Mobile Hotspot:移动热点,就是将设备当成了无线路由器,时刻发送信号帧。不同的是,其通过蜂窝网络将设备连接至互联网。
Section 10: Network Security
Section 11: Data Flow Example
用户于主机访问网站流程:用户连接家庭 WLAN 并通过 DHCP 获得私网 IP。浏览器输入域名后发送 DNS 查询获取服务器 IP。系统将 HTTP 请求依次封装成 TCP 段、IP 包和链路层帧,通过 ARP 找到网关后送往路由器。路由器执行 NAT 并将数据转发到互联网。服务器处理请求并返回响应。路由器再将响应映射回私网 IP,笔记本解封装并由浏览器渲染网页。流程图展示如下:
1 | 用户接入WLAN → DHCP分配IP → 浏览器输入域名 |
Module 3: Introduction to Networking
Section 1: Networking Overview
URL 和 FQDN 区别 :FQDN,完全合格域名,告诉你应期望到达的服务器在哪;而 URL 不仅包含 FQDN,还告知期望的是服务器中的哪个资源。
Section 2: Network Types
Section 3: Networking Topologies
Section 4: Proxies
Forward Proxy:前向代理,Client → 配置代理 → Forward Proxy → Internet。客户端不解析域名、不直接连目标服务器,而是先发给代理服务器。
Reverse Proxy:反向代理,Internet → Reverse Proxy → 后端真实服务器。互联网中暴露的 IP 其实是反向代理服务器的 IP,而不是服务器的。
Section 5: Networking Models
Section 6: The OSI Model
Section 7: The TCP/IP Model
Section 8: Network Layer
Class |
Network Address | First Address | Last Address | Subnetmask | CIDR | Subnets | IPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A |
1.0.0.0 | 1.0.0.1 | 127.255.255.255 | 255.0.0.0 | /8 | 127 | 16,777,214 + 2 |
B |
128.0.0.0 | 128.0.0.1 | 191.255.255.255 | 255.255.0.0 | /16 | 16,384 | 65,534 + 2 |
C |
192.0.0.0 | 192.0.0.1 | 223.255.255.255 | 255.255.255.0 | /24 | 2,097,152 | 254 + 2 |
D |
224.0.0.0 | 224.0.0.1 | 239.255.255.255 | Multicast | Multicast | Multicast | Multicast |
E |
240.0.0.0 | 240.0.0.1 | 255.255.255.255 | reserved | reserved | reserved | reserved |
Section 9: Subnetting
Section 10: MAC Addresses
MAC 地址构成:MAC 地址共有六个字节组成,前三个字节是 IEEE(电气和电子工程师学会)为各制造商定义的 OUI(组织唯一标识符)。后三个字节称为 NIC(网络接口控制器),由制造商分配。第一个八位元组的最后两位(第7、8位)还能发挥另一个重要作用。第 7 位表示它是由 IEEE 定义的全局 OUI(0), 还是本地管理的 MAC 地址(1)。第 8 位将 MAC 地址识别为单播 (0,发送的数据包只会到达一个特定的主机)或多播 (1,发送一次给本地网络上的所有主机)。
通信双方在同一个子网:局域网内,传输会直接发送到目标计算机的物理地址。
1 | 1、判断:源主机通过对比目标 IP 地址和自己的子网掩码,发现目标主机在同一个本地网络。 |
通信双方在不同子网:跨网络时,会发送至默认网关,即路由器处。
1 | 1、判断:源主机通过对比目标 IP 地址和自己的子网掩码,发现目标主机在一个远程网络。 |
Address Resolution Protocol:ARP,地址解析协议,它将主机的 IP 地址映射到对应的 MAC 地址。当设备希望与局域网上的另一设备通信时,会发送 ARP 请求,将目标设备的 IP 地址解析为其 MAC 地址。请求会广播给局域网上的所有设备,并包含目标设备的 IP 地址。拥有匹配 IP 地址的设备会响应其 MAC 地址。当设备收到 ARP 请求时,会向请求设备发送带有 MAC 地址的 ARP 回复。回复消息包含请求端和响应端设备的 IP 和 MAC 地址。
1 | 0.000000 10.129.12.100 -> 10.129.12.255 ARP 60 Who has 10.129.12.101? Tell 10.129.12.100 |
ARP 缓存中毒:指的是攻击者将指定 IP 与自身设备 MAC 地址关联,从而有效拦截该合法设备的流量。比如:
1 | 0.000000 10.129.12.100 -> 10.129.12.101 ARP 60 10.129.12.255 is at CC:CC:CC:CC:CC:CC (ARP reply from attacker claiming gateway IP) |
Section 11: IPv6 Addresses
Section 12: Networking Key Terminology
这里仅记录网站原文,并未详细学习。
| Protocol | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Wired Equivalent Privacy | WEP |
WEP is a type of security protocol that was commonly used to secure wireless networks. |
| Secure Shell | SSH |
A secure network protocol used to log into and execute commands on a remote system |
| File Transfer Protocol | FTP |
A network protocol used to transfer files from one system to another |
| Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | SMTP |
A protocol used to send and receive emails |
| Hypertext Transfer Protocol | HTTP |
A client-server protocol used to send and receive data over the internet |
| Server Message Block | SMB |
A protocol used to share files, printers, and other resources in a network |
| Network File System | NFS |
A protocol used to access files over a network |
| Simple Network Management Protocol | SNMP |
A protocol used to manage network devices |
| Wi-Fi Protected Access | WPA |
WPA is a wireless security protocol that uses a password to protect wireless networks from unauthorized access. |
| Temporal Key Integrity Protocol | TKIP |
TKIP is also a security protocol used in wireless networks but less secure. |
| Network Time Protocol | NTP |
It is used to synchronize the timing of computers on a network. |
| Virtual Local Area Network | VLAN |
It is a way to segment a network into multiple logical networks. |
| VLAN Trunking Protocol | VTP |
VTP is a Layer 2 protocol that is used to establish and maintain a virtual LAN (VLAN) spanning multiple switches. |
| Routing Information Protocol | RIP |
RIP is a distance-vector routing protocol used in local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs). |
| Open Shortest Path First | OSPF |
It is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) for routing traffic within a single Autonomous System (AS) in an Internet Protocol (IP) network. |
| Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | IGRP |
IGRP is a Cisco proprietary interior gateway protocol designed for routing within autonomous systems. |
| Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | EIGRP |
It is an advanced distance-vector routing protocol that is used to route IP traffic within a network. |
| Pretty Good Privacy | PGP |
PGP is an encryption program that is used to secure emails, files, and other types of data. |
| Network News Transfer Protocol | NNTP |
NNTP is a protocol used for distributing and retrieving messages in newsgroups across the internet. |
| Cisco Discovery Protocol | CDP |
It is a proprietary protocol developed by Cisco Systems that allows network administrators to discover and manage Cisco devices connected to the network. |
| Hot Standby Router Protocol | HSRP |
HSRP is a protocol used in Cisco routers to provide redundancy in the event of a router or other network device failure. |
| Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol | VRRP |
It is a protocol used to provide automatic assignment of available Internet Protocol (IP) routers to participating hosts. |
| Spanning Tree Protocol | STP |
STP is a network protocol used to ensure a loop-free topology in Layer 2 Ethernet networks. |
| Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System | TACACS |
TACACS is a protocol that provides centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting for network access. |
| Session Initiation Protocol | SIP |
It is a signaling protocol used for establishing and terminating real-time voice, video and multimedia sessions over an IP network. |
| Voice Over IP | VOIP |
VOIP is a technology that allows for telephone calls to be made over the internet. |
| Extensible Authentication Protocol | EAP |
EAP is a framework for authentication that supports multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, digital certificates, one-time passwords, and public-key authentication. |
| Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol | LEAP |
LEAP is a proprietary wireless authentication protocol developed by Cisco Systems. It is based on the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) used in the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). |
| Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol | PEAP |
PEAP is a security protocol that provides an encrypted tunnel for wireless networks and other types of networks. |
| Systems Management Server | SMS |
SMS is a systems management solution that helps organizations manage their networks, systems, and mobile devices. |
| Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer | MBSA |
It is a free security tool from Microsoft that is used to detect potential security vulnerabilities in Windows computers, networks, and systems. |
| Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition | SCADA |
It is a type of industrial control system that is used to monitor and control industrial processes, such as those in manufacturing, power generation, and water and waste treatment. |
| Virtual Private Network | VPN |
VPN is a technology that allows users to create a secure, encrypted connection to another network over the internet. |
| Internet Protocol Security | IPsec |
IPsec is a protocol used to provide secure, encrypted communication over a network. It is commonly used in VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, to create a secure tunnel between two devices. |
| Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol | PPTP |
It is a protocol used to create a secure, encrypted tunnel for remote access. |
| Network Address Translation | NAT |
NAT is a technology that allows multiple devices on a private network to connect to the internet using a single public IP address. NAT works by translating the private IP addresses of devices on the network into a single public IP address, which is then used to connect to the internet. |
| Carriage Return Line Feed | CRLF |
Combines two control characters to indicate the end of a line and a start of a new one for certain text file formats. |
| Asynchronous JavaScript and XML | AJAX |
Web development technique that allows creating dynamic web pages using JavaScript and XML/JSON. |
| Internet Server Application Programming Interface | ISAPI |
Allows to create performance-oriented web extensions for web servers using a set of APIs. |
| Uniform Resource Identifier | URI |
It is a syntax used to identify a resource on the Internet. |
| Uniform Resource Locator | URL |
Subset of URI that identifies a web page or another resource on the Internet, including the protocol and the domain name. |
| Internet Key Exchange | IKE |
IKE is a protocol used to set up a secure connection between two computers. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs) to provide authentication and encryption for data transmission, protecting the data from outside eavesdropping and tampering. |
| Generic Routing Encapsulation | GRE |
This protocol is used to encapsulate the data being transmitted within the VPN tunnel. |
| Remote Shell | RSH |
It is a program under Unix that allows executing commands and programs on a remote computer. |
Section 13: Common Protocols
Section 14: Wireless Networks
Section 15: Virtual Private Networks
VPN 简介:允许私有网络与远程设备之间实现安全且加密的连接。这使得远程机器能够直接访问私有网络,提供对网络资源和服务的安全且机密的访问。VPN 通常使用 TCP/1723 端口用于点对点隧道协议 PPTP 的 VPN 连接,UDP/500 端口用于 IKEv1 和 IKEv2 的 VPN 连接。
Section 16: Vendor Specific Information
虚拟局域网的实现逻辑: